Published on July 16, 2020 by Vivek Mishra
The COVID-19-induced lockdowns that stalled a number of polluting activities helped us realise how beautiful a pollution-free world is. However, as governments relax restrictions and economic activity returns, demand for energy and, in turn, pollution would increase. Hence the significant buzz around adopting clean technology when the crisis ends.
Coal and its uses
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock and our most abundant fossil fuel. It is used in the form of coke for metallurgical processes, such as steel making, and as steam or thermal coal for generating power. It is also essential in the production of specialist products, such as activated carbon, silicon metal and carbon fibre.
Challenges in coal power use
Coal is composed mainly of carbon, with smaller amounts of other elements such as sulphur, mercury, lead and arsenic. Burning coal releases mercury, lead and arsenic into the environment, increasing air pollution. Coal combustion also releases considerable carbon dioxide (CO2) – one of the main greenhouse gases – into the atmosphere, adding to global warming.
Coal is, therefore, one of the major sources of CO2 emissions. CO2 released through coal combustion is responsible for over 0.3°C of the 1.0°C increase in global average annual surface temperature above pre-industrial levels, according to a US Energy Information Administration (EIA) report. Coal-fired power generation was the largest emitter in 2018, accounting for around 30% of all energy-related CO2 emissions.
Introduction to clean coal technology
Various technologies are being developed to reduce the negative environmental effects of power generation from coal and climate change. The collection of such technologies is known as clean coal technology (CCT).
One such emission-reduction technology that has been introduced is carbon capture, use and storage (CCUS). This technology involves the capture of waste CO2 from coal combustion and its transportation via ship or pipeline for safe use or storage, preventing it from entering the atmosphere.
Carbon Capture Utilization & Storage Routes
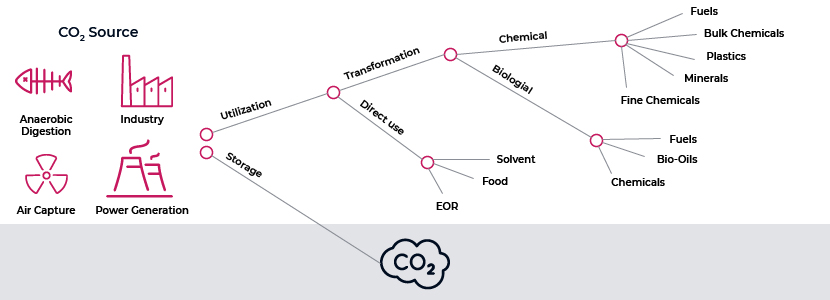
EOR: Enhanced oil recovery
Why CCUS?
The world requires clean and reliable power generation technology, and CCUS technology is expected to play a critical role in the sustainable transformation of the industrial sector.
-
Cost-effective: CCUS is one of the most cost-effective solutions available for reducing emissions from industrial and fuel transformation processes (to produce a relatively pure stream of CO2, such as natural gas and hydrogen produced from fossil fuels). CCUS technology can be applied to these facilities at as low as USD15-25 per tonne of CO2.
-
Reduces emissions: CCUS technology accounts for almost one-fifth of the emission reduction needed in the industrial sector, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA). It is estimated that 28 giga tonnes of CO2 (GTCO2), 31GTCO2 and 56GTCO2 will be captured through CCUS technology from the iron and steel, fuel transformation and power sectors, respectively, by 2060.
-
Decarbonises: Using CCUS technology is especially important to decarbonise (remove carbon compounds released by) industrial processes
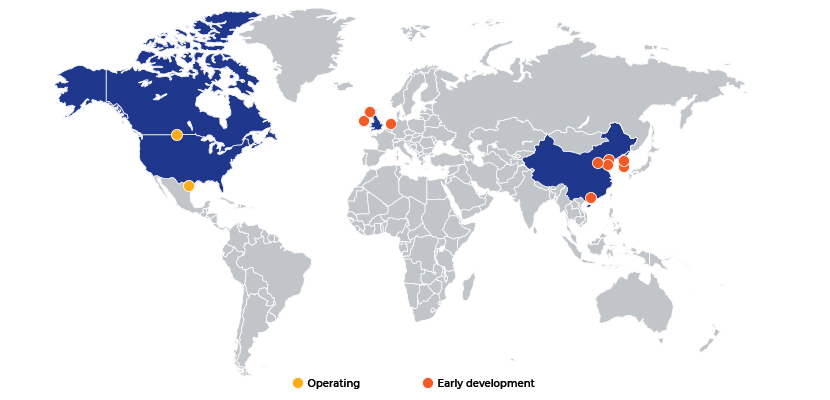
Nine CCUS power generation projects are currently in early development, according to the Global CCS Institute’s CO2RE database: four in China, two in Korea, and one each in the UK, Ireland and the Netherlands.
Global CCUS Projects - 2019
Measures to achieve the goal
The World Coal Association (WCA) outlines the actions required for greater international commitment to advancing CCUS technology:
-
90 large-scale CCUS facilities would need to come online each year from 2020 to 2050 to reach the 2,732 CCUS facilities needed by 2050
-
National governments could award grants through competitive procurement to encourage pre-competitive storage appraisal activity
-
Mobilise finance to boost CCUS opportunities. CCUS technology is currently eligible for funding through the Green Climate Fund (which supports the efforts of developing countries in dealing with climate change) and the Global Environment Facility (which tackles our planet's most pressing environmental problems)
-
The WCA will undertake research and development activity to advance the technology to make the CCUS process more efficient
How Acuity Knowledge Partners can help
Increasing awareness of CCT has led to heavy investment in the technology, with the US and Europe at the forefront. Industry experts believe that with the growing influence of impact investing, the future belongs to CCT. To make the CCT process more effective and efficient, industries that produce CO2, such as electric utilities, steel mills and cement plants, would have to follow the WCA’s suggestions. We at Acuity Knowledge Partners take pride in our energy-sector experts. We offer services such as project evolution, partnership search, market sizing, essential value chain support and financial research and analysis to established and new companies.
Sources:
World Coal Association (WCA)
International Energy Agency (IEA)
iamrenew.com
carbonnext.eu
Tags:
What's your view?
About the Author
Vivek has over five years of experience in delivering various market research projects by implementing secondary research, market forecasting, and data skills. He is graduated in Bachelor of Technology in Mechanical Engineering from Anand Engineering College, Agra. At Acuity Knowledge Partners, he works in Mining & Metals industry, with special focus on analyzing 'Coal’ and 'Uranium' as a commodity across the globe.
Comments
17-Jul-2020 04:33:38 am
Excellent presentation, precisely summed up and a what a simple n easy language you have written in. Really helpfull. Keep it up, Vivek !!
17-Jul-2020 06:35:01 am
CCUS technology is the demand of present and future and hope so whole world is taking eco friendly energy considerationa now and this should be a great step for this conventional source of energy. Good beginning Vivek Bhai ?
Like the way we think?
Next time we post something new, we'll send it to your inbox








