Published on April 18, 2025 by Ankit Agrawal
-
Germany’s incoming Chancellor Friedrich Merz announced a new spending package focusing on the infrastructure and defence sectors, aiming to modernise the economy and enhance security
-
The plan has been approved by parliament, making way for c.EUR1tn (23% of GDP) in additional investment over the next decade, with a strong focus on Germany infrastructure spending to modernize key sectors and drive long-term economic growth.
-
The spending plan will likely boost annual economic growth to 1.5-2% by 2027 compared to economic contraction in both 2023 and 2024
-
Despite the expected deterioration in Germany's fiscal profile due to higher deficits (an additional 1.5-2.5 percentage-point increase in the fiscal deficit/GDP ratio annually), the country has ample fiscal capacity to support an increase in spending without risking its debt sustainability
Germany is set to embark on a transformative journey with a significant increase in infrastructure and defence expenditure. Incoming Chancellor Friedrich Merz's financial package, which eliminates Germany's long-standing constitutional debt break rule, aims to revive the nation's economy and enhance its defence capabilities. The incoming government plans to invest c.EUR1tn in defence and infrastructure over the next decade.
The spending plan marks a significant shift in Germany's fiscal policy by relaxing stringent controls on government borrowing and potentially stimulating the struggling economy. Increased defence spending will likely provide a cyclical boost to the economy, while the proposed infrastructure package will result in long-term gains in GDP growth.
The financial package comprises three major pillars:
-
An off-budget infrastructure fund, which is authorised to borrow up to EUR500bn over 12 years, with EUR100bn to be allocated to the Climate and Transition Fund and EUR100bn to be distributed to states for regional projects
-
Defence spending exceeding 1% of GDP or c.EUR43bn (based on 2024 nominal GDP) to be exempt from constitutional borrowing restrictions
-
The 16 German states are allowed to borrow up to 0.35% of GDP, equivalent to c.EUR15bn (according to 2024 nominal GDP of EUR4.3tn), instead of being required to maintain balanced budgets
Modernising Germany's infrastructure: a path to economic revival
Germany's long-neglected infrastructure has been in need of modernisation, and the incoming government aims to address this critical issue through the new spending plan. The investment will target key areas such as transport, energy and digital infrastructure, aiming to create a more efficient, sustainable and connected Germany.
The large infrastructure spending will also have a significant economic impact over the medium to long term given its multiplier effect. These investments are expected to generate employment, stimulate private-sector investment and improve overall productivity and competitiveness.
Defence spending: strengthening Europe's security
In response to the US policy change, Germany plans to significantly increase its Germany defence spending to bolster its defence capabilities by investing in advanced weapons hardware and systems, and cybersecurity measures, ensuring long-term national security and strategic stability. This marks a paradigm shift in Germany's defence policy, highlighting the need for a robust and modern military in the ever-evolving geopolitical landscape. Moreover, strengthening Germany's defence capabilities would contribute to the overall security of Europe and reinforce the region's stability.
Despite an expected substantial increase in defence spending, the short-term economic impact of the spending is less clear, as significant dependence on imported defence equipment has resulted in a weakening of the domestic defence sector. Nevertheless, the new package will enable the government to commit to long-term procurement, potentially driving higher private investment in the sector. Therefore, defence spending will add only modestly to economic growth in the near term, but the long-term prospects remain attractive.
Economic revival: the impact of fiscal stimulus
The German economy has contracted over the past two years, shrinking 0.3% y/y in 2023 and 0.2% y/y in 2024, as weakened consumer sentiment affected private consumption while muted domestic and foreign demand for manufactured goods affected investment. Nevertheless, the latest infrastructure and defence spending plans are expected to have a substantial impact on economic growth. The fiscal stimulus is designed to counteract economic stagnation and provide a much-needed boost to a number of sectors. In the short term, the fiscal stimulus will likely counteract the stagnation forecast for 2025 due to President Trump’s tariffs and boost annual economic growth to 1.5-2% by 2027.
The spending announcement has already boosted investor confidence, with the ZEW Indicator of Economic Sentiment rising to 51.6 in March 2025 from 26 the previous month. This surge in confidence reflects positive market sentiment and expectations of future economic stability and growth.
Leveraging fiscal capacity
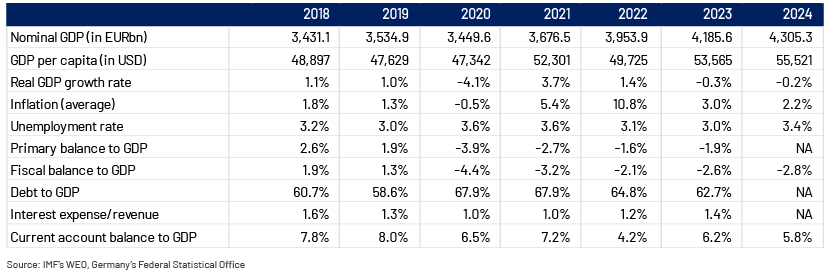
Germany’s debt/GDP was 62.5% in 2024, highlighting its ample fiscal capacity to support the planned increase in military and infrastructure expenditure. It is estimated that the government will undertake EUR1tn in additional spending over the next decade. The new expenditure is likely to be scaled up gradually. As such, fiscal deficit/GDP will likely widen to c.4.5% by 2027 from 2.8% in 2024, while debt/GDP could widen to 70% by 2027.
Although Germany’s debt will be one of the highest among AAA-rated names’ (median at 36.5%, according to Fitch), this is not a concern, as its large, diversified economy enhances its debt-carrying capacity. The country's strong economic fundamentals and diversified industrial base provide a solid foundation for managing higher debt levels. In addition, the government’s high debt affordability (interest expenses to revenue of 1.4% in 2023) and large national savings (30% of GDP in 2023) support the country’s debt sustainability. These factors ensure that Germany can comfortably service its debt without compromising fiscal stability. Furthermore, its debt is subscribed to by a diversified investor base, reducing refinancing risk for the government. This broad investor base includes both domestic and international investors, providing stability and confidence in Germany's fiscal management.
Market reaction was mixed to Germany's new spending package:
-
Stock market rallied: European equities, particularly German stocks, saw a significant rally following the announcement. Investors are optimistic about the potential for renewed economic growth. Benchmark German index DAX jumped c.4.5% following the announcement, although it subsequently shed all the gains.
-
Sector impact: Shares of defence companies have surged, reflecting the anticipated boost in defence spending. Prospects for metal and steel manufacturers, as well as the mechanical engineering sector and financials, have improved.
-
-
Bond-market reaction:German government debt experienced a sharp sell-off due to the prospect of increased government debt issuance and fiscal easing. This caused the yield on benchmark 10-year bonds to surge nearly 40bps to 2.9%, the highest level since late 2023. Although yields have since decreased to around 2.7%, they remain above the 2.5% level prior to the announcement.
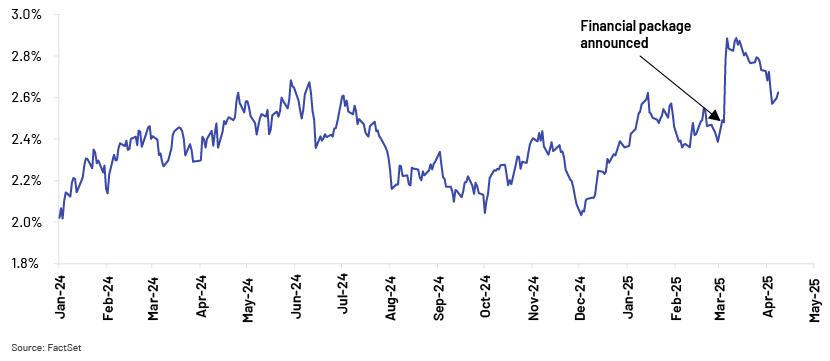
-
Business sentiment: Germany's business sentiment saw a strong rebound in March 2025, driven by renewed momentum in the manufacturing sector and expectations of fiscal stimulus. The IFO Business Climate Index rose to 86, its highest in seven months, up from 85.3 in February 2025, aligning with expectations.
Conclusion
Germany's substantial fiscal package reflects a proactive approach to addressing geopolitical and growth challenges. These measures demonstrate a strong commitment to bolstering the economy and enhancing infrastructure. While there are risks to its fiscal situation, the potential for increased economic growth and improved competitiveness is significant. The political landscape and structural economic issues will play a crucial role in shaping the effectiveness of these measures, but the overall outlook is optimistic.
Key macroeconomic indicators
How Acuity Knowledge Partners can help
Acuity Knowledge Partners support asset managers, hedge funds and other financial institutions invested in the sovereign, sub-sovereign, corporates and municipals space. Our expertise spans comprehensive investment research, leveraging both qualitative and quantitative fundamental credit research. By integrating advanced technological solutions, we enhance our speed to market and deliver actionable insights that drive informed decision-making. Our team of highly experienced in-house subject-matter experts ensures that we deliver unparalleled support, helping clients navigate complexities and capitalise on emerging opportunities across regions and sectors.
Sources:
-
IMF’s World Economic Outlook
-
FactSet
-
Fitch
-
€1 trillion impact: What easing debt brake means for Germany – DW – 03/17/2025
-
German business morale surges to 7-month highs on recovery hopes | Euronews
What's your view?
About the Author
Ankit has close to 12 years of experience in fixed income credit research, focusing on bank, sovereign and corporate credit reviews. He has worked with three of the largest buy-side asset managers, based in Europe and the US, assisting with investment decisions. He is actively involved in discussing themes and issuer updates and is adept at writing detailed credit reviews and building in-depth financial models to present his investment case. Ankit holds a Master of Business Administration (Finance) from Symbiosis International University.
Like the way we think?
Next time we post something new, we'll send it to your inbox










