Published on October 22, 2024 by Ajit Singh
Decarbonisation, demographics and deglobalisation, supported by the increased role of private investments, are expected to propel growth of India’s economy.
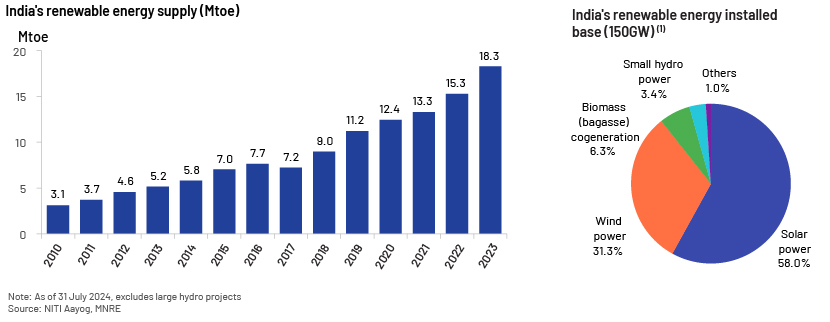
Current situation of renewable energy in India
India has very low electricity consumption per capita – only 1,331KWh (as of FY 2023) – compared to that of many developed countries (global average: 3,664KWh), indicating significant potential given changing lifestyles and rising levels of income/consumption. The government aims to meet a substantial portion of increasing demand with renewable energy, backed by public-private partnerships (PPPs) and other forms of private investment.
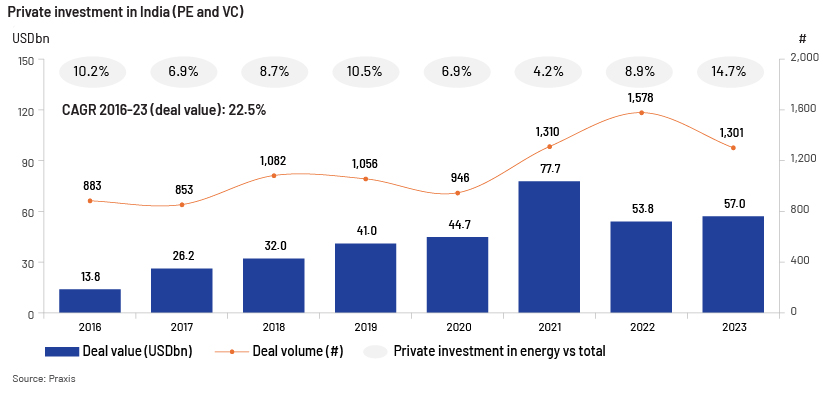
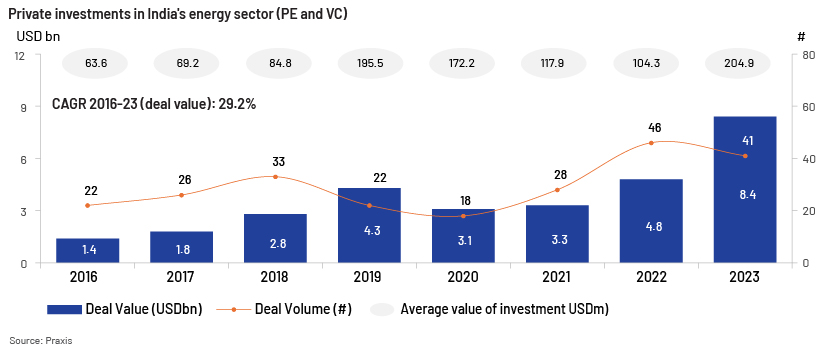
Private investment in India (with a focus on the renewable energy sector)
Private investment in India has grown considerably – 16.5% since 2010 – increasing from USD7.8bn in 2010 to USD57.0bn in 2023 and peaking at USD77.7bn in 2021, with significant investments in the energy sector amounting to USD8.4bn in 2023. Most private investment in the electricity sector was concentrated on the renewable energy sector – accounting for 100% in 2020, 81% in 2021, 100% in 2022 and 79% in 2023.
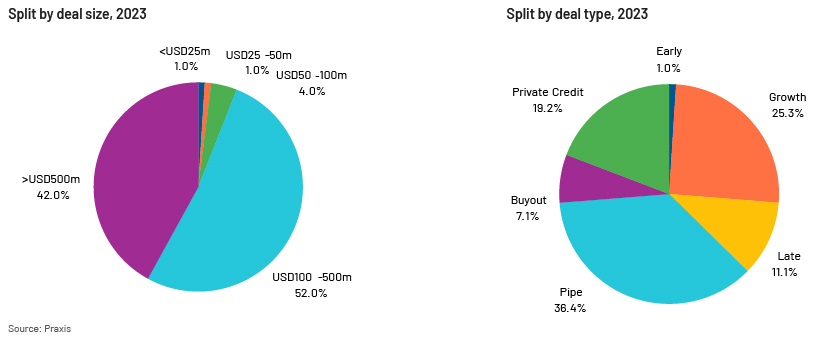
Some key investments
| Company | Funding (USDm) | Stage | Investors | Remarks |
| 200.0 | -- | |
July 2024: Option to inject a further USD350m of incremental equity capital to support growth of the business | |
 |
~35.9 | -- | July 2024: Aimed at increasing the company’s production capacity | |
| 700.0 | Pipe | June 2023: To support growth through the development of new renewable energy projects, including low-risk expansions of existing wind farms | ||
| 650 | Growth |  |
May 2023: To support the company to achieve 4,000MW of installed renewable energy capacity | |
| 1,070.0 | Growth | April 2023: To fund manufacturing of green hydrogen and green ammonia ventures in India |
Green hydrogen – an emerging sector
The generation of hydrogen using renewable sources has gained popularity in recent time and become a focal point for investment in the renewable energy sector. Green hydrogen is generated through electrolysis of water, and the electricity used for the process is obtained through renewable sources; the gas is used mainly as an industrial/domestic fuel and an input to industries
-
The National Green Hydrogen Mission aims to produce 5 MMTPA of green hydrogen by 2030, requiring 125GW of renewable energy. India mainly produces grey hydrogen (from fossil fuels) for consumption at present.
-
Investment of USD180-200bn is expected by 2030, considering the government’s and private players’ targets/announcements. USD100bn is expected to be invested to meet the current target of producing 5MMPTA and the balance to develop related infrastructure/ecosystem.
-
The bulk of this investment is to come from private players in refineries, fertilisers and related industries to meet their decarbonisation efforts.
-
Investment from venture capital (VC) firms and private equity (PE) investors could be targeted for providing early-stage funding for startups and companies developing technologies in the green hydrogen sector.
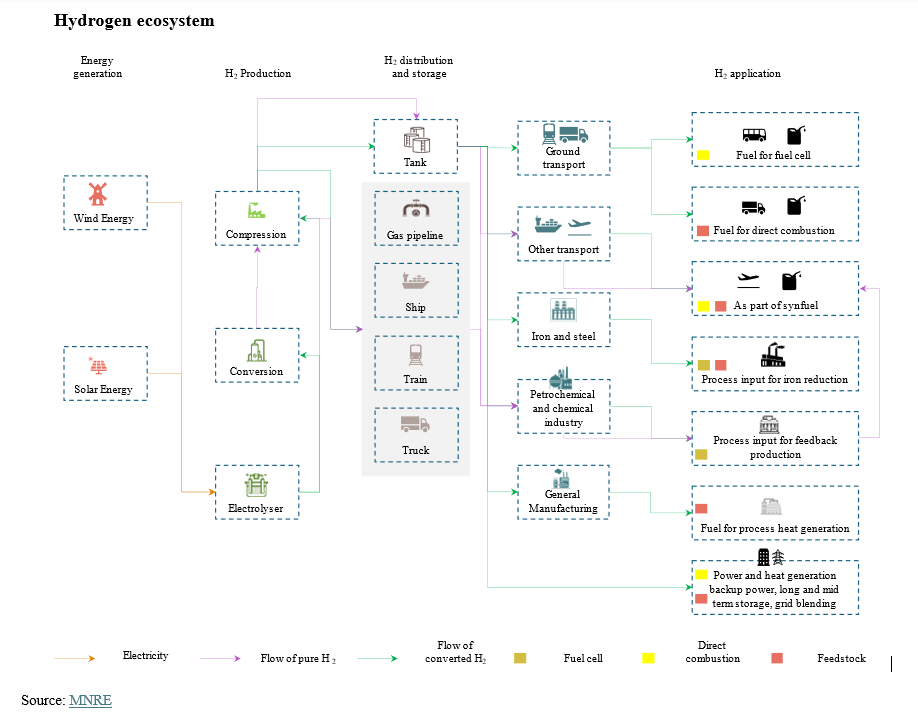
Key sectors running pilot projects include steel, domestic application, aviation, railways, container vessels and refineries. Most of these pilot projects are targeted for application in the transport sector or as an alternative fuel as the country aims to improve its energy security and meet its emissions target
Application in transport
-
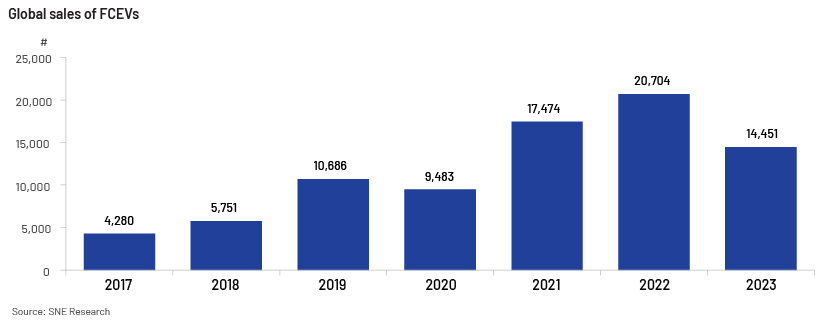
Its major application at present is in fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs), a type of EV that uses hydrogen gas (green hydrogen) to generate electricity and power the electric engine. Global adoption of the FCEV market increased in recent years before registering a decline in 2023. Overall market penetration has been lower than that of traditional EVs.
-
There are no FCEVs for sale in India currently; the application is still in pilot stage, with projects backed mainly by the government
-
On 25 September 2023, Tata motors delivered FCEV buses to IOCL
-
On 3 February 2023, Indian Railways (IR) announced plans to run 35 hydrogen trains under the “Hydrogen for Heritage” project at an estimated cost of USD9.5m per train and ground infrastructure of USD8.3m per route on a number of heritage/hill routes
-
India’s key investments/announcements
The government of India and many other private and public enterprises have announced significant investments, including the following:
-
22 February 2024: NTPC to set up a green hydrogen project in Vishakhapatnam, India
-
14 February 2024: Avaada Green H2, to invest USD952m to set up a 0.5 Mtpa green hydrogen/ammonia facility in Odhisa, India
-
28 August 2023: TCPL, a joint venture between Tata and Cummins, set up to develop and manufacture sustainable technology products including hydrogen-powered internal combustion engines and fuel-cell electric systems. In March 2024, a new manufacturing facility to produce hydrogen-based internal combustion engines for medium - and heavy-duty commercial vehicles was set up in Jamshedpur, India
-
7 February 2023: Reliance Industries Limited and Ashok Leyland launch India’s first hydrogen internal combustion engine-powered heavy-duty truck
-
17 March 2022: Toyota, in collaboration with the International Centre for Automotive Technology (iCAT), starts a pilot project to evaluate the performance of Toyota Mirai on Indian roads and climatic conditions
Conclusion
Hydrogen is abundantly available, but it still has miles to go before it can be accepted as a regular source of clean energy in India’s ecosystem. It is a great alternative to EVs due to its high range, quick refuelling and being a good substitute for lithium, which is limited in availability. However, manufacturing it has its own challenges: it is an energy-intensive process, requiring high upfront outlay, leading to high refuelling costs.
Green hydrogen is still in the initial stages development, lacking supportive infrastructure, robust technology and safety guidelines. To make it the fuel of the future, the government, together with industry players, must provide investment support in the form of incentives and favourable policies. Providing R&D and innovation support, and developing a roadmap and strategies for growth, supported by an established regulatory regime, would impact the growth story positively.
How Acuity Knowledge Partners can help
With two decades of experience in delivering research and analytics services, we have built a robust and sustainable ecosystem of people, process and technology. We have strong credentials within the private equity segment, supporting private equity players across the value chain. We provide customised solutions to clients across the private equity sector.
Sources:
-
Niti Aayog
-
MNRE
-
https://www.praxisga.com/PraxisgaImages/ReportImg/india-private-investments-report-2024-Report-3.pdf
-
https://cea.nic.in/wp-content/uploads/general/2024/General_Review_2024_2.pdf
-
https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/per-capita-electricity-generation
-
https://www.reuters.com/article/markets/gic-adia-invest-230-mln-in-indian-renewable-energy-firm
-
https://static.pib.gov.in/WriteReadData/specificdocs/documents/2024/may/doc2024510336301.pdf
-
https://www.deccanherald.com/specials/investments-of-180-200-billion-in-green
What's your view?
About the Author
Ajit Singh is part of the Private Equity & Consulting team at Acuity Knowledge Partners. He has 4+ years of experience in research, and currently supports private equity clients with research assignments including initiation and thematic reports, economic updates, data research and company presentations. He holds a Master’s degree in Business Economics
Like the way we think?
Next time we post something new, we'll send it to your inbox









