Published on May 3, 2018 by Vipul Gupta
The global financial crisis led to the run on Northern Rock in September 2007 and the collapse of Lehman Brothers in September 2008. The UK Government gave support packages for Lloyds Banking Group after its acquisition of HBOS, and the Royal Bank of Scotland, in October 2008 (~£65bn bailout). As part of its response to the crisis, the UK Government established the Independent Commission on Banking (ICB), led by Sir John Vickers, to recommend banking reforms to promote financial stability and competition in the United Kingdom. Ring-fencing was the central recommendation of the ICB and was introduced through the Financial Services (Banking Reform) Act 2013.
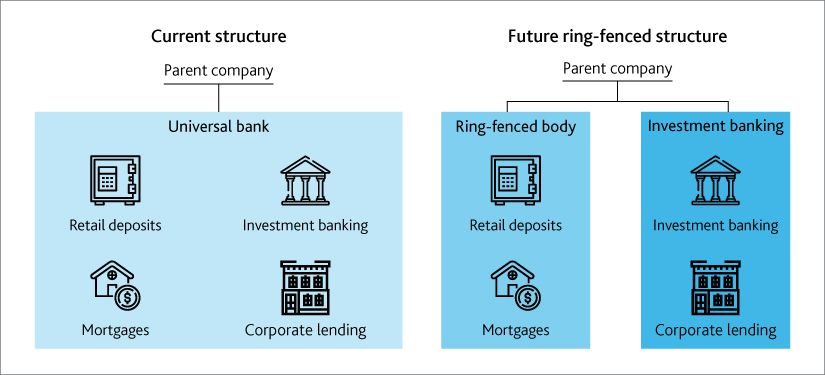
From 1 January 2019, the largest UK banks must separate core retail banking from investment banking. This is known as ring-fencing. The idea is that the essential (retail) parts of the business will become safer, making it less likely that normal people will be affected by a failure in the riskier parts, such as investment banking. The rules are aimed at the biggest 5 lenders - HSBC, RBS, Lloyds, Santander UK and Barclays, as well as any challengers who climb above the £25bn deposit mark (3 year average of more than £25bn ‘core deposits’ - broadly from individuals and small to medium-sized businesses).
Overall structural changes:
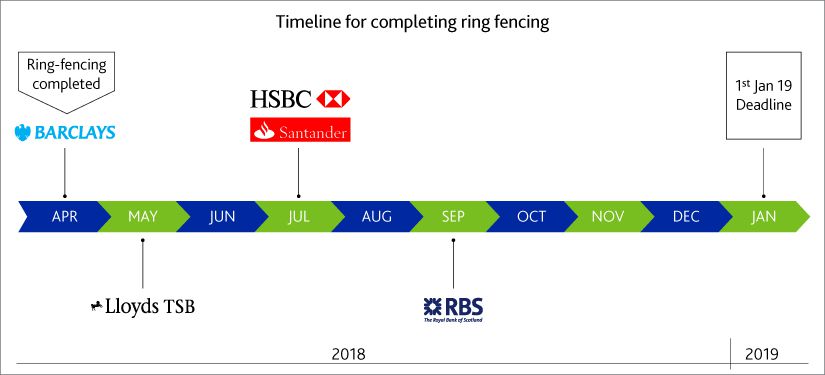
Barclays is the first UK bank to complete ring-fencing effective 1st Apr 2018 with approx. costs of £1bn. Barclays' new stand-alone UK bank has 24m customers and £250bn of assets. Below is the tentative timeline for completion of ring fencing provided by respective banks. Basis this it appears all major banks will be able to comply with regulation well in time.
Benefits
-
The regulations are meant to protect British consumers and businesses from the fallout if there is another financial crisis. The idea is that if a lender’s investment bank were to fail, the UK retail arm would have its own capital and separate IT systems and remain safe
-
Ring-fencing will support financial stability by making banking groups simpler and easier to ‘resolve’. It will be easier to manage the failure in an orderly way without the need for a government bail-out
Downside
-
It is not cheap to implement. Ring fencing has increased the regulatory costs for the UK banks. As per one estimate, banks will need to spend an estimated £200m each to implement the reforms, and then additional £120m per year sustaining the extra staff in areas like IT, HR and risk. Barclays ring fence has cost it around £1bn
-
Further, regulators can ask banks to hold additional capital basis its risk assessment of the bank's loans portfolio (upto 12.5pc of risk weighted assets)
To conclude, separating retail banking services is just one aspect of reforms to make the system safer. Ring-fencing alone cannot protect a bank from a collapse in its retail banking business – the crisis which brought down the UK’s former building societies in the credit crunch. Neither Bradford and Bingley nor Northern Rock had investment banking operations. Ring-fencing represents an important part of the response to the financial crisis and meeting the objectives of ending ‘too big to fail’ and preventing the costs of bank failures falling on taxpayers.
The solutions offered by Acuity Knowledge Partners Investment Banking and Commercial Lending business enable banks to tackle regulatory and other business challenges successfully and enhance profitability.
Sources:
FCA – Financial Conduct Authority
Tags:
What's your view?
About the Author
Vipul Gupta has over 16 years of experience in working with leading global organisations in the banking and commercial lending domains. His expertise spans a broad range of credit analysis, financial modelling, portfolio management, leveraged lending, industry coverage and onshore client-facing roles. Vipul holds an MBA in Finance and a bachelor’s in mechanical engineering.
Like the way we think?
Next time we post something new, we'll send it to your inbox











