Published on November 8, 2022 by Huankun Zhao and Yuxin Zhang
Factors driving the proliferation of lithium-ion batteries
Since Sony commercialised lithium-ion batteries in 1990, they have gained substantial market share. Compared with other energy storage devices, lithium-ion batteries have the advantages of high energy density and long cycle life.
However, traditional lithium-ion batteries have critical safety issues because they use highly flammable organic liquid electrolytes or polymer electrolytes. These electrolytes have low thermal stability and low flame points, and easily cause fire accidents and explosions if used improperly. [1]
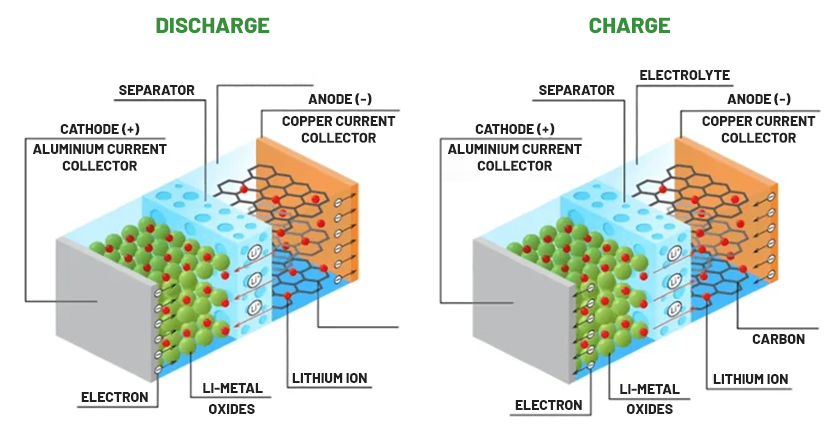
Working mechanism of a lithium-ion battery [2]
https://www.azom.com/article.aspx?ArticleID=19013
Developing direction of lithium-ion batteries – solid-state lithium-ion batteries
To thoroughly address the safety issues, the use of highly flammable organic liquid electrolytes should be avoided entirely; all-solid-state batteries (ASSBs) become a good choice because organic liquid electrolytes are replaced by inorganic solid electrolytes that have high thermal stability.
Advantages of using ASSBs:
-
As no liquid electrolyte is used, packaging for ASSBs can be simplified, reducing dead weight in battery packaging and increasing energy density.
-
Inorganic solid electrolytes have much better electrochemical stability than organic liquid electrolytes and polymer electrolytes, and are compatible with higher potential cathode materialsto increase energy density.
-
ASSBs have excellent mechanical properties. [3]
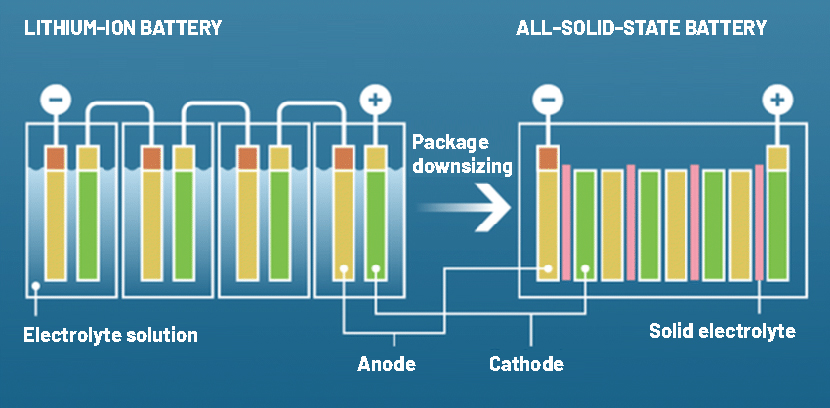
Difference between traditional lithium-ion batteries and solid-state batteries [4]
Disadvantages of using all-solid-state batteries:
Although all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries have many advantages, there are also several technical problems.
-
On one hand, solid-state batteries do not use liquid electrolytes, so the ionic conductivity would be greatly reduced, making it difficult to achieve fast charging. On the other hand, internal resistance of the solid electrolyte interface (solid-solid) is large. Larger internal resistance means the battery’s energy loss is higher and more heat will be generated.
-
Even if the technical problems are solved, the cost of production needs to be reduced before production of large volumes could start. The price of raw materials for solid-state lithium-ion batteries is currently five times more than that of raw materials for traditional lithium-ion batteries. Besides, production of solid-state lithium-ion batteries requires high purity of raw materials, which translates into significant investment in equipment. [5]
All these issues would need to be resolved before the production of large volumes could start, and resolution may take 5-10 years.
The semi-solid-state lithium-ion battery – the compromise
A semi-solid-state lithium-ion battery is a battery where one electrode contains liquid electrolytes while the other electrode contains no liquid electrolytes. From the view of percentage of weight, liquid electrolytes account for 20% of a traditional lithium-ion battery’s weight, but 10% of a semi-solid-state lithium-ion battery’s weight. [6]
Advantages of using semi-solid-state batteries:
Semi-solid-state lithium-ion batteries have the following advantages over traditional lithium-ion batteries:
-
higher energy density
-
better performance in low temperatures
-
higher security
-
longer service life
Semi-solid-state lithium-ion batteries have the advantage of lower cost and technical bar over all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries.
Disadvantages of using semi-solid-state batteries:
Semi-solid-state lithium-ion batteries have the following disadvantages over all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries:
-
less energy density
-
worse performance in high temperatures
Given that the most important application of lithium-ion batteries is powering electric vehicles, the semi-solid-state lithium-ion battery is more attractive. Semi-solid-state lithium-ion batteries also support a satisfactory range of capacity. It is widely recognised that the upper limit of capacity for traditional lithium-ion batteries is 300 Wh/kg, while first-generation semi-solid-state lithium-ion batteries could achieve capacity of 400 Wh/kg. For automobiles, safety and cost are the main factors that affect consumers’ and manufacturers’ decisions. Semi-solid-state lithium-ion batteries, therefore, seem to be the best choice.
How Acuity Knowledge Partners can help
We support companies active in investing, developing and promoting clean energy and cleantech solutions. We work together with our clients’ strategy, product and business development and commercial teams, leveraging our industry research and consulting experience, bespoke end-to-end support and dedicated working models. We deliver critical insights, run analyses, evaluate strategic transactions and partnerships, and build business models and collateral in a cost-efficient manner, so clients can benefit from operational efficiencies.
References:
-
Review on solid electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries, Journal of Power Sources, Volume 389, 15 June 2018, Pages 198-213
-
Samsung Unveils Groundbreaking All-solid-state Battery Technology – BusinessKorea
What's your view?
About the Authors
Huankun Zhao works as an industry research analyst in Acuity Beijing. He is currently providing industry research support for a global firm, focusing on new energy area. He holds a master’s degree in Materials Science & Engineering from Washington University in St. Louis.
Yuxin Zhang works as an associate in Acuity Beijing office. She is currently supporting Li ion Battery industry research for a global firm. She has a master’s degree of applied finance in Pepperdine University. She previously worked as a teller in HSBC.
Like the way we think?
Next time we post something new, we'll send it to your inbox