Published on July 7, 2021 by Abhishek Gupta
Introduction:
Current guidance on accounting for convertible instruments is inherently complex, leading to multiple errors and complications in its application. On 5 August 2020, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) issued Accounting Standards Update (ASU) 2020-06, Debt – Debt with Conversion and Other Options (Subtopic 470-20), simplifying the accounting process for certain financial instruments with convertible features. Subsequently, FASB Vice Chairman James L Kroeker stated that, “The ASU 2020-06 is an important step in simplifying a complex area of accounting guidance that has been a frequent source of financial restatements. We expect it to improve comparability of information for financial statements users and reduce cost and complexity for preparers and auditors.”
The ASU significantly modifies current guidance on issuers’ accounting for convertible instruments, resulting in fewer convertible instruments requiring separate recognition.
Convertible instruments:
Convertible instruments, typically bonds or preferred stock, are debt or equity instruments that provide the investor the right to convert them into equity securities of the issuer. The accounting treatment of these instruments depends on the underlying terms and conditions, including how the instrument is settled upon conversion. Additionally, convertible instruments may contain provisions such as call and put options, and contingent interest. These provisions need to be evaluated to assess whether the accounting process should involve bifurcation of these provisions.
Amendments:
The guidance on convertible instruments contains multiple classifications and measurement requirements under various accounting standards, based on multipart sets of classification and measurement as stipulated by ASC 470 – Debt, ASC 480 – Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity, ASC 815 – Derivatives and Hedging, and ASC 825 – Financial Instruments.
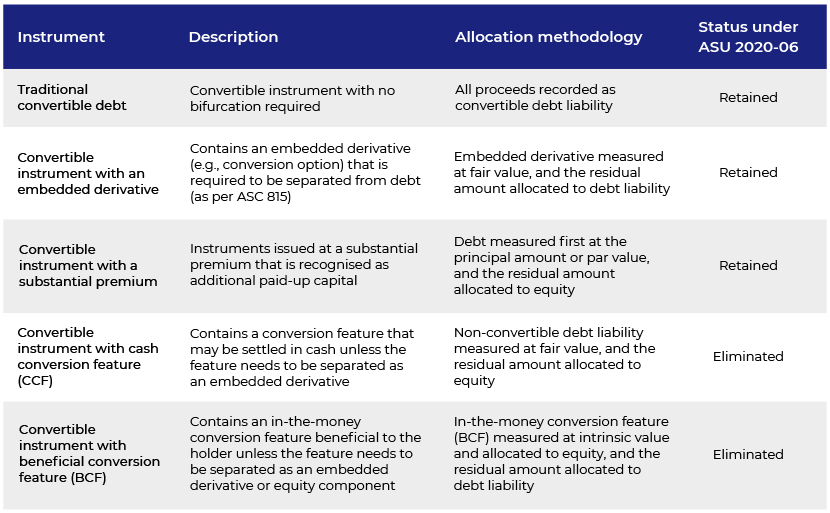
There are five existing models under the current guidance for proceeds allocation at the issuance of a convertible instrument, i.e., (1) Traditional convertible debt model, (2) Embedded derivative model, (3) Substantial premium model, (4) Cash conversion feature model and (5) Beneficial conversion feature model. ASU 2020-06 focuses on simplifying the complexity in the accounting process by disposing of the more complex features, i.e., the cash conversion feature (CCF) and the beneficial conversion feature (BCF).
The following table briefly summarises each accounting model and its status under ASU 2020-06:
Effective dates and early adoption:
The amendments in this update are effective for public business entities that meet the definition of a Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) filer, excluding entities eligible to be smaller reporting companies as defined by the SEC, for fiscal years beginning after 15 December 2021, including interim periods within those fiscal years. For all other entities, the amendments are effective for fiscal years beginning after 15 December 2023, including interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted, but no earlier than fiscal years beginning after 15 December 2020, including interim periods within those fiscal years. The board specified that an entity should adopt the guidance as of the beginning of its annual fiscal year.
An entity that has not yet adopted the amendments in Accounting Standards Update No. 2017-11, Earnings Per Share (Topic 260), Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity (Topic 480), Derivatives and Hedging (Topic 815): (Part I) Accounting for Certain Financial Instruments with Down Round Features and (Part II) Replacement of the Indefinite Deferral for Mandatorily Redeemable Financial Instruments of Certain Non-public Entities and Certain Mandatorily Redeemable Non-controlling Interests with a Scope Exception can early-adopt the amendments in this update for convertible instruments that include a down round feature. This early adoption is permitted for fiscal years beginning after 15 December 2019.
Author’s insight on key takeaways:
The amendment simplifies accounting for convertible instruments, as more contracts will be accounted for as traditional convertible debt instruments and will qualify for equity classification
The interest rate of convertible debt instruments will be closer to the coupon rate than the higher interest rate resulting from the separation of the convertible’s features
The interest expense for the convertible instruments will be lower
More convertible instruments will be eligible for the fair value option under ASC 825
The amendment may significantly reduce the effort and time required to determine whether an embedded derivative feature can be exempt from derivative accounting
How Acuity Knowledge Partners can help
Our dedicated team of experienced professionals with deep domain knowledge and extensive financial modelling and valuation capabilities help clients derive the fair value of convertible instruments and embedded derivatives in accordance with up-to-date accounting standards and guidance. We also support clients on multiple business combinations/purchase price allocation engagements under ASC 805 and goodwill impairment engagements under ASC 350 for tax and financial reporting purposes. Additional key services we offer include valuation of complex financial instruments, fund accounting services, Section 409A, fair value measurements, stock-based compensation, legal-entity valuations and portfolio valuations.
Our years of experience in valuing instruments using comprehensive financial modelling and up-to-date valuation techniques have helped us develop best practices and consider all scenarios.financial accounting advisory outsourcing
For more details, please visit our Valuations page.
References:
1) FASB Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2020-06, Debt – Debt with Conversion and Other Options (Subtopic 470-20) and Derivatives and Hedging – Contracts in an Entity’s Own Equity (Subtopic 815-40): Accounting for Convertible Instruments and Contracts in an Entity’s Own Equity
Tags:
What's your view?
About the Author
Abhishek holds over 10 years’ total experience, leading and supervising a wide range of valuation projects in compliance with various accounting standards, such as ASC 820 (loan portfolios, debt and related embedded derivatives and convertible notes), IRC 409A (preferred stocks, common stocks, options, warrants, incentive units, etc.), ASC718/IFRS2 (PSUs, MIUs, profit interests and ESOPs) and ASC805/IFRS 3 (contingent considerations).
Prior to joining Acuity Knowledge Partners, Abhishek worked at higher managerial levels with Ernst and Young and Credit Suisse, and assisted alternative asset managers and corporates on various valuation-related assignments. He has significant experience in developing complex statistical and probabilistic valuation models, such as Black-Scholes, Binomial Lattice,..Show More
Like the way we think?
Next time we post something new, we'll send it to your inbox









