Published on August 23, 2024 by Meghana D Prakash
SMEs are generally defined based on parameters such as annual sales, number of employees, number of assets owned, market capitalization or other features that can be used to gauge the size of the company, but mainly include the employee strength below 250. SMEs greatly outnumber the large-scale companies operating worldwide. In sectors including retail, manufacturing, e-commerce or online business and freelancing, which require few employees and limited capital, SMEs continue to strive drawing material interest from lenders, investors and business owners. According to The World Bank, SMEs make up around 90% of the businesses globally, 50% of global employment and 40% of gross domestic product in emerging markets.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, in 32 countries, 70-80% of SMEs lost 30-50% of their revenue and faced challenges in managing their fixed cost, creating a global economic impact that unlocked various lending and financial opportunities for the SMEs. SME lending is not only economically important but also the most profitable to lending and banking institutions.
According to The World Bank, SMEs across the world have annual unmet financial needs to the tune of USD5.2 trillion, or 1.5x the size of the current SME lending market. Various trends and opportunities are set to help SMEs perform to their full potential and contribute to sustainable economic development.
Major trends and opportunities in SME lending
Digital transformation: The pandemic has shown the potential of digitalisation in the ever-evolving business landscape. Digital lending has simplified lending, offering numerous benefits (including speedier approval of credit to SMEs) compared to traditional lending. As SMEs today seek faster and more convenient borrowing options, commercial lenders are compelled to modernise their operating systems to sustain a competitive edge and adapt to market dynamics.
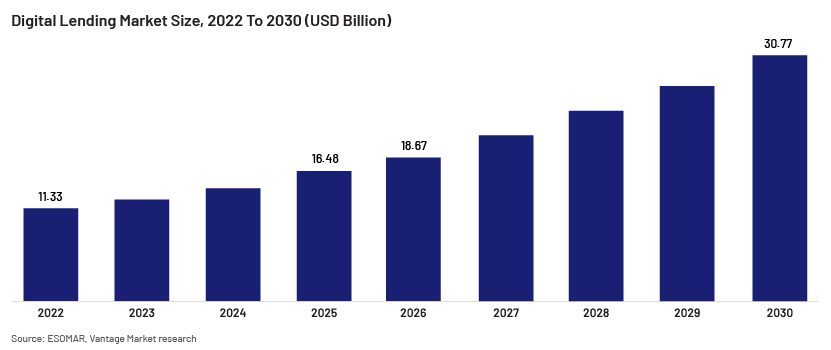
According to ESOMAR, the European Society for Opinion and Marketing Research, the global market for digital lending in 2022 was USD11.33bn; it expects the market to grow to USD30.77bn by 2030, clocking a compound annual growth rate of 29.15% over this period.
The revolution in traditional lending practices has helped SMEs seamlessly navigate the journey from application to fund disbursement and easy access to essential credit lines. This allows commercial lenders to meet growing demand and enhance SMEs’ experience through artificial intelligence-driven credit assessment and block-chain-powered loan origination. This also helps lenders in the form of more efficient and accurate credit analysis, underwriting and portfolio management.
Cross-border financing: Cross-border lending opens new markets and opportunities for SMEs to grow beyond borders. As businesses are interconnected on a global scale, there is growing demand for cross-border SME lending solutions. With the help of international partnerships and digital platforms, lenders can facilitate financing for SMEs engaged in international trade and expansion incentives.
Regulatory support: Over the years, SMEs have created ample jobs and supported the major economies worldwide. As a result, governments of many countries are implementing supportive policies and initiatives to stimulate SME lending to promote innovation and growth, enhance public trust and foster international trade and investment. Regulatory support includes the following:
-
Tax incentives – Tax incentives are provided to SMEs by governments to encourage them to continue their business in the long term, which will likely be beneficial for the economy. This was first started by the Japanese government in 1998.
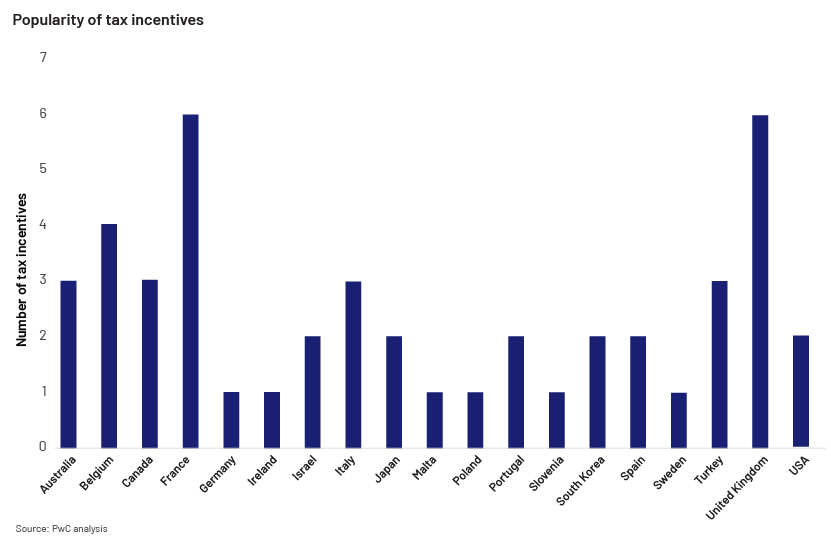
Countries that offer tax benefits to SMEs believe that preferential tax treatment leads to significant job creation and enhanced risk-taking, speed, flexibility, and innovation in entrepreneurship. According to PWC – PricewaterhouseCoopers International Limited, there has been rapid growth in early investment in the UK and France, due to the polarity of tax incentives and tax breaks for angel investors (see chart below).
-
Direct capital injection – Direct capital injection serves as a growth catalyst for SMEs and financial aid. Additional funds improve SMEs’ liquidity, which can be deployed for the repayment of borrowings, business expansion, etc. The Development Bank of India (DBI) in 2022-2023 alone disbursed over USD7.7bn (INR55,000 crore) to micro, small and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) under various schemes. Fund infusion through such channels empowers businesses to evolve, increase hiring and contribute to the economy.
-
Innovation grants – These are financial awards provided by federal, state or local governments to SMEs, which they can use as capital to start and expand their businesses.
Small Business Technology Transfer, The National Science Foundation in the US and Small Business Innovation Research are a few grants that have created over 600,000 jobs and led to significant technological advancements.
-
Simplified regulations: Following regulations and ensuring compliance require time and resources, which are often limited for SMEs. Hence, the government is streamlining the business registration process by simplifying regulations. As per The World Bank, a 10% reduction in the time required for commencement drives a 2-3% increase in the number of firms established.
Impact investing: Lenders are focused on making a difference by ensuring their lending practices comply with environmental, social and governance (ESG) criteria and supporting SMEs dedicated to driving positive change.
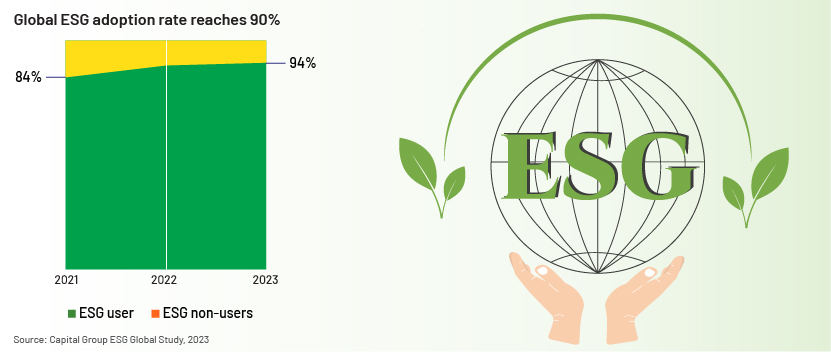
The share of investors worldwide that view ESG as supportive investing increased to 90% in 2023 (see chart below), creating opportunities for SMEs to access funds from investors and drive economic sustainability on a global scale.
Fintech development: The fintech industry’s remarkable growth in recent years has reshaped the SME financing landscape. During the COVID-19 pandemic, online alternative finance platforms experienced a staggering 57% y/y increase in the funding volume, highlighting their resilience and importance in providing crucial support to SMEs, as per a 2023 Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) report.
Moreover, survey data from Southeast Asian countries reveals that a significant portion of users on these platforms are sole traders (78%) and young companies, aged 1-5 years (56%). These data insights collectively illustrate how the fintech industry’s development has democratised access to capital, streamlined lending processes and fostered innovation in SME financing.
Conclusion
SMEs today are driving innovation and growth, making significant contributions and advancements across various sectors. Their progress is fuelled by digital-lending transformation, improved cross-border financing, supportive regulatory policies, rise of impact investing and expansion in fintech to meet the unmet financial needs of SMEs. Globally, SMEs navigate a diverse set of approaches and operational challenges. Developed countries (including the US, the UK and Germany) focus on robust regulatory and technological support. Meanwhile, developing countries (including India, Kenya and Indonesia) leverage fintech to enhance financial inclusion. Each country’s approach reflects the unique challenges impacting its economy and shaping a dynamic and evolving global lending landscape for SMEs.
How Acuity Knowledge Partners can help
At Acuity Knowledge Partners, we provide tailored financial solutions to clients to help them make informed decisions and manage risks efficiently. Our services include:
-
Market research analysis: We identify and analyse key trends, opportunities and challenges in an ever-evolving lending landscape
-
Financial spreading and underwriting: This includes detailed analysis of business performance.
-
Know-your-customer services: This covers risk-rating of clients, due diligence and transaction tracking.
-
Portfolio management and monitoring: This encompasses monitoring loan performance, formulating loss mitigation strategies and financial modelling.
Sources
-
MSME Lending 2024: Market Opportunity and Differentiator Strategy (leadsquared.com)
-
Small business, big impact: how SMEs are embracing sustainability - Cogito COGITO (oecdcogito.blog)
-
Financing SMEs and Entrepreneurs 2024: An OECD Scoreboard | en | OECD
-
How banks can reimagine lending to small and medium-size enterprises | McKinsey
Tags:
What's your view?
About the Author
Meghana D Prakash is associated with Acuity Knowledge Partners for over 2 years, specializing in lending services. She has worked in collateral, financial spreading, valuation, fund administration and other lending operations projects for international banking and financial companies.
Meghana holds an MBA in Finance and Human Resources from BNMIT, under VTU University, and a BCom in Accounting from Dayananda Sagar Institution, affiliated with Bangalore University.
Like the way we think?
Next time we post something new, we'll send it to your inbox









