Published on September 20, 2021 by Neha Singh
The manufacturing industry entered a new paradigm with the adoption of Industry 4.0. The healthcare industry is similarly on the verge of venturing into a world of smart and connected healthcare that would revolutionise the way healthcare is delivered across the globe.
Rapid technological advancement and the COVID-19 pandemic have accelerated growth of all aspects of the healthcare industry, including patients, providers and investors. But where is this heading? Advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), the internet of things (IoT), robotics and virtual reality (VR) are integrating with healthcare services to help providers in areas such as working more efficiently, keeping patients connected using wearables and other tools for remote patient monitoring, using robotics to introduce specialty care and assisting surgeons during operations. Apart from helping healthcare providers, these technologies improve the quality of life of larger populations and reduce healthcare expenditure.
Telehealth will only advance, further accelerating its influence in the healthcare industry.
AI in telehealth
The use of AI in telehealth is enabling clinicians to make real-time, rich, data-driven decisions, a major factor in enhancing the patient journey and creating better health outcomes.

AI is being used or can be used in several areas of telehealth:
-
Virtual consultation: AI is being used to advance or accelerate the initial patient screening process, so that during the physical visit, the provider’s time would be spent only on providing treatment. It also helps primary-care doctors easily locate the best specialist to meet a patient’s needs in line with their healthcare policies, and provides easy access to clinical information by maintaining records across all platforms and the value chain.
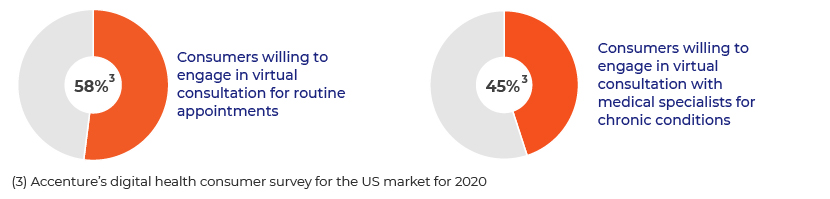
-
Diagnostic assistance: Helps physicians make medical decisions. With AI, they are able to extract large amounts of information on patients with similar illness profiles from monitoring devices or medical telemetry products to produce algorithmic patterns that can suggest potential next steps and enhance a physician’s ability to provide treatment.
Example: Researchers at the Mount Sinai Health System developed an AI algorithm to rapidly detect COVID-19 by integrating patients’ chest CT scans with clinical information including symptoms, age, blood reports and possible contact with infected people. The algorithm follows the physician workflow used to detect COVID-19 and provides a final analysis using separate probabilities of CT images, clinical data and both combined. The AI system also detected 68% of COVID-19-positive cases in situations where radiologists interpreted those cases as negative due to the negative CT appearance.
IoT in telehealth
Telehealth combined with IoT is enabling healthcare providers to offer excellent healthcare through real-time diagnosis and treatment. IoT applications connect smart devices, machines, patients, doctors and sensors to the internet in an efficient and smart manner, facilitating remote monitoring, chronic disease management and elderly care of remote patients and even caring for institutionalised patients by remaining connected to the internet.
-
Remote patient monitoring (RPM): IoT has made remote monitoring of patients possible, helping doctors access a patient’s details every second through connected devices and sensors. The pandemic has forced healthcare providers to reinvent their practices to accommodate patients, and RPM has become a coveted solution by offering an ideal opportunity to monitor and treat infected patients from afar, isolating them while giving doctors and nurses the opportunity to treat more patients at a safe distance. This use of IoT in telehealth would be helpful for senior citizens under care, patients with chronic diseases getting care at home and patients in rural areas.
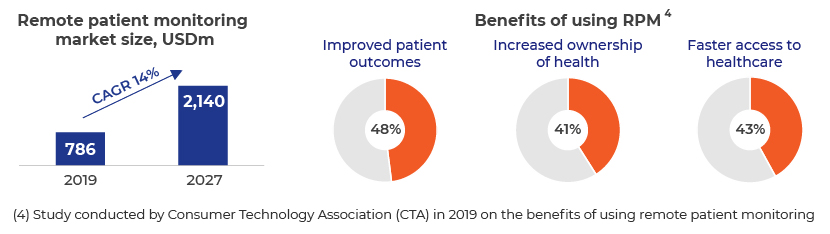
-
Smart medical devices: With the market for remote patient monitoring expanding, adoption of smart devices and wearables has risen. Smart medical devices are enhancing current telemedicine practices by collecting patient data, transferring it to the patient’s physician and integrating it into electronic health records. Care providers can now access a patient’s health data through connected devices outside of the conventional care setting. A number of devices can transmit biometric data from wearables or remote monitoring devices, such as pulsometers, blood pressure cuffs and sensor-embedded clothing, and can be used to monitor health problems such as pulmonary disorders, cardiac disorders and neurodegenerative disorders.
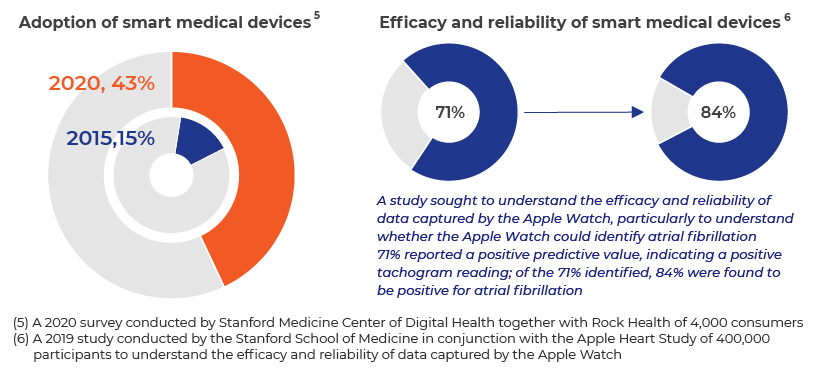
Apart from just incorporating raw patient health data into physician-facing reports and interfaces, a combination of AI, predictive analytics and RPM enables proactive identification, intervention and care for the patient.
Pandemic impact on adoption of telehealth
The COVID-19 pandemic has forced all entities in the healthcare industry to promote the use of digital technologies. Telehealth has provided a way to care, and now offers a chance to reinvent virtual and partially virtual care models, to provide improved access to healthcare.
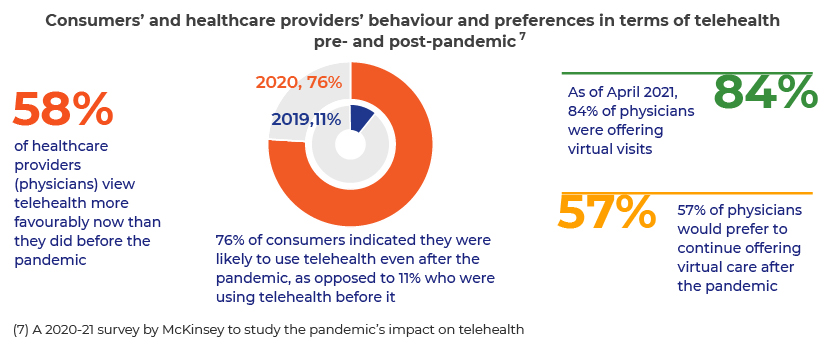
The pandemic has demonstrated the significance of telehealth, paving the way to modernise the healthcare delivery system with the acceptance of all stakeholders in the healthcare industry.
Apart from wide acceptance among consumers and healthcare providers, growth in telehealth is also evident from the significant investment in the space over the past year, driven by the pandemic.
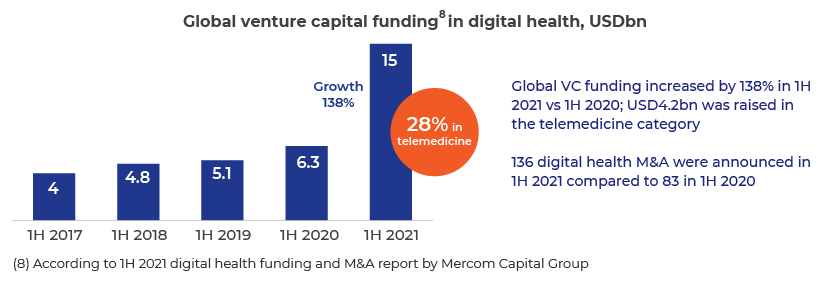
Telehealth has come a long way since the outbreak of the pandemic, from increased utilisation of telehealth services and stabilisation by 2021, improved perceptions of consumers and health providers compared to before the pandemic, regulatory changes facilitating the use of telehealth and significant investment in digital health to evolving tech solutions and business models. We expect growth to stabilise, although the market still has a long way to go.
Conclusion
The fundamental factors applicable to any sector – new solutions to problems, technological advancement, changing market sentiment and consumer preferences, and strong investment flow – would drive growth of telehealth as well.
Telehealth has a much broader use, beyond video chats – to support complex care for patients both in hospital and at home.
Data-driven connected devices and care solutions can give providers access to patient insights anytime, anywhere, helping them determine the most appropriate course of action for care delivery.
The use of AI- and IoT-powered remote patient monitoring systems amid the current crisis will likely serve as a precedent for healthcare facilities across the globe, paving the way for the standardisation of diagnostic assistance and remote patient care and improving patient outcomes.
Moving beyond the pandemic, these solutions will likely continue to enable faster, quality care while keeping patients in the comfort of their homes, other safe spaces or at hospitals.
For this to succeed, however, all participants in the healthcare sector, including providers, payers and patients, must work to integrate this advanced version of telehealth into the existing environment to upgrade delivery of healthcare. We expect more technological advancement, more new products and services and increased adoption of telehealth in the near future.
How Acuity Knowledge Partners can help:
Leveraging nearly two decades of experience in analysing historical information and predicting trends, we help our clients, including life sciences and healthcare firms, build and strengthen their strategies and business.
We also provide services such as therapy area landscapes, opportunity prioritisation, lifecycle management and go-to-market and market assessment.
For more information on our capabilities, please visit our Life sciences solutions page.
Sources:
https://medcitynews.com/2021/06/remote-patient-monitoring-coming-of-age-in-an-ai-driven-world/
https://tataelxsi.com/storage/insights/January2021/RUM2GYMFdMUJZwuC8O34.pdf
https://www.accenture.com/_acnmedia/PDF-130/Accenture-2020-Digital-Health-Consumer-Survey-US.pdf
https://www.prescouter.com/2021/03/how-are-smart-medical-devices-enhancing-telemedicine/
https://www.healthrecoverysolutions.com/blog/telehealth-integration-of-wearables
https://rockhealth.com/reports/digital-health-consumer-adoption-report-2020/
https://mercomcapital.com/product/1h-q2-2021-digital-health-healthcare-it-funding-ma-report/
Tags:
What's your view?
About the Author
Neha Singh has over 7 years of experience in the research and consulting industry. She currently works in the Strategy Research and Consulting practice at Acuity Knowledge Partners and supports consulting and corporate clients in their research & strategy assignments. She is experienced in customized research related to market & competitive intelligence, market assessment, benchmarking, competitive landscape, market entry & growth strategy, partner identification in addition to others. She has exposure and knowledge of proprietary databases such as Capital IQ, Preqin, Thomson, Orbis and Merger Market.
Prior to Acuity Knowledge Partners, she was working with a Management Consulting firm, where she worked closely with clients across..Show More
Like the way we think?
Next time we post something new, we'll send it to your inbox









