Published on March 28, 2023 by Goshaleea Rasathurai
“If your business is not on the internet, then your business will be out of businesses” – Bill Gates
The internet has evolved over the years. Imagine an internet that not only depicts your inputs, but also customises the data in line with your personal preferences. This is what Web 3.0 does. But what is Web 3.0? It is the third generation of web technologies, which has now become an integral part of the technological world. Web 3.0 is still in evolution stage, expanding into decentralised applications and making wide use of blockchain-based technologies, machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI). Web 3.0 applications include non-fungible tokens (NFTs), decentralised finance (DeFi), cryptocurrency, dApp, cross-chain bridges and decentralised autonomous organisations (DAOs). Two applications that currently use Web 3.0 are Siri and Wolfram Alpha.
Origin of Web 3.0
Web 3.0 is an extended version of Web 1.0 and 2.0. Web 1.0 (World Wide Web: read-only web) is static website content with information delivery and centralised infrastructure. Users connect to websites via search engines such as Google and Internet Explorer to view and download content with read-only functionality. Web 2.0 (read-write web) is a centralised user-input version with social networks and cloud utility infrastructure. This includes websites and applications that use user-generated content. The problem with Web 2.0 is that all the data is saved in a centralised system. In contrast, Web 3.0 (read-write-interact web) is a metaverse world with decentralised, edge computing, peer-to-peer and blockchain-based distributed services. This is focused on providing relevant content for each user through machine learning and AI on the Semantic Web, sometimes known as Web 3.0.

Key aspects of Web 3.0
A feature of Web 3.0 is decentralisation, where applications and services are enabled in a distributed manner without a central authority. In previous versions, computers search for data in a fixed location, usually in a single server. In this new technology, information is stored in several locations and can be extracted based on content. As decentralisation is based on blockchain, data and connection across services are distributed in a different manner than if it were a centralised database infrastructure. This would also enable an immutable ledger of transactions and activity that supports providing verifiable authenticity in a decentralised world.
As a result of decentralisation, the network would enable participants to interact directly, without a trusted intermediary (trust-less) and without authorisation from a governing body (permission-less). In addition, users will be able to sell their own data through decentralised data networks and help maintain ownership control. Unlike in previous versions, users do not need to rely on centralised organisations such as Facebook and Google.
AI and machine learning play a vital role – Web 3.0 understands information based on Semantic Web concepts and natural language processing, similar to humans, and uses data and algorithms to improve accuracy. This will result in automation, producing more relevant, unbiased data and enhanced data connectivity. For example, online review platforms help customers review any product or service. However, a company could also pay to create positive reviews for products that do not deserve to be promoted. This is where AI supports in terms of differentiating the biased data from the unbiased to provide more reliable information.
Connectivity and ubiquity in Web 3.0 enable everyone to access the internet at any time and from anywhere from internet of things (IoT) technology through new types of smart devices. Hence, internet-connected devices will no longer be required to be limited to certain computers and smartphones, as Web 3.0 will allow for the development of a multitude of new devices.
Moreover, spatial web and 3D graphics blur the line between the physical and digital via graphics and 3D virtual worlds. 3D will enhance gaming applications and help sectors such as real estate, healthcare and e-commerce excel in their respective fields.
Superiority of Web 3.0
Data encryption is one of the major advantages of Web 3.0, providing greater control over personal data due to decentralisation and permission-less systems that limit data extraction (information collected from web users without their consent). This prevents large data organisations such as Google and Apple from controlling users’ personal information for their own interests. Moreover, with Web 3.0, users are required to have only one profile for use on any platform. Hence, users have full control over their personal data.
Web 3.0 has the potential to provide greater utility beyond social media and online shopping, overriding Web 2.0. Open-source blockchain systems enable collaborative design and development. With decentralisation, data accessibility (seamless services) has increased, giving users multiple backups to avoid server crashes.
Web 3.0 also creates an unrestricted platform for users to interact with the network. Users are not restricted based on location or social factors, enabling them to transfer their wealth across the world in no time. This would increase application in new areas and improve user interactions through the Semantic Web, AI and machine learning.
Web 3.0 is useful for problem solving and heavy knowledge-generation tasks. Large processing capacity helps provide products and services with high value addition. For instance, in Web 3.0, machines can help users with decision making and content creation such as planning and process execution automatically. Similarly, virtual assistance can help plan trips and assist with housekeeping and home security. For example, virtual assistance can help plan a holiday – from obtaining discounted tickets to making hotel reservations.
Pitfalls of Web 3.0
Web 3.0 development could increase legal and regulatory risks. Cybercrime, hate speech and misinformation could rise due to a decentralised structure. Enforcing regulation would become more difficult, as globally hosted website content cannot be governed by country-specific laws.
Even though Web 3.0 is intelligent, efficient and more accessible than previous generations, the technology is not ready for general use. This creates uncertainty about widespread adoption. Similarly, advanced devices are required for the technology to reach a large number of people. Therefore, device capabilities need to be expanded to make the technology accessible from anywhere. Complicated functionality could also cause issues in the adoption of Web 3.0. Cutting-edge technologies such as AI and blockchain may be difficult for older generations to master, and some may find it difficult to afford advanced devices.
The easy availability of user information and less anonymity create demand for reputation management. Companies need support from customers in gaining market intelligence and business insights, and adopt internet marketing to overcome the complications inherent in the process. Hence, a company needs to maintain its reputation, resulting in demand for reputation management.
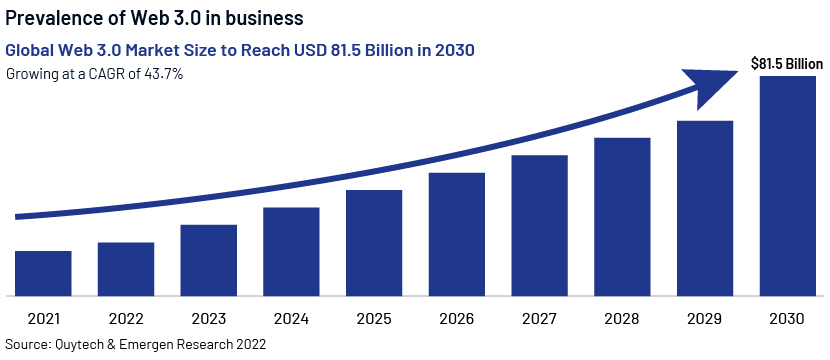
Web 3.0 supports and impacts business in numerous ways. It is vital that businesses invest in Web 3.0, as the technology is growing exponentially. The following are areas in which businesses can capitalise on the new web technology:
Customer relationship management (CRM) – Understanding customer needs is key to delivering customised services. Data availability is limited by traditional CRM methods. The evolution of Web 3.0 will open the way to a wide range of new data sources through which businesses can understand their customers in depth to offer tailor-made services; this would also transform the way businesses interact with customers.
Data management – Web 3.0 will create new value propositions and offer new services to data-driven businesses. This increased use of data would result in a better understanding of customers to meet their requirements effectively.
Marketing and advertising – Web 3.0 will revolutionise marketing by enhancing the personalised experience. Marketing would be more successful when the target audience can be reached effectively through a customised experience. This would increase sales and brand awareness, enabling a company to stay ahead of the competition.
Fintech – Uninterrupted service, faster transactions, automated data processing, mutual trust and new opportunities are benefits of implementing Web 3.0. Demand for call centres can be reduced, fraud detection improved and financial lending services decentralised. These are just some of the advancements generated by this new era of web technology.
Personalisation – Real-time data integration could accelerate online transactions. Implementing the correct business model would enhance the customer experience and potential for advertising and promotion.
Supply-chain management – The shift from traditional supply chains to decentralised supply-chain networks would be through making supply chains more efficient and secure, reducing costs and improving the quality of products and services. Streamlined business processes enabled by Web 3.0 include maintaining transaction ledgers for the parties involved and automating contracts using smart contracts.
Transforming the financial services space
All banking and lending services were previously controlled by centralised systems, and customers had to interact with financial intermediaries for loans and mortgages. The decentralised finance system introduced by Web 3.0 eliminates the need for financial institutions to govern financial services. This results in accessible, open, free and fair financial markets to everyone with an internet connection.
The financial sector would see new client groups and marketplaces. Thus, it is vital that financial institutions capitalise on the advantages of Web 3.0. They should employ AI to automate operations, reduce costs and increase income. Eighty-three percent of the finance professionals surveyed believe AI is critical for success, according to a recent survey by NVIDIA. Some of the benefits of using Web 3.0 in bank operations to accelerate access to trading intelligence are a reduction in the number of client calls, faster application delivery and accurate fraud prediction.
Banks can influence customers through tracking changes in consumer trends and providing a hyper-personalised experience based on digital footprint by integrating customer lifestyles. Banks should invest in digital innovation and transform customers’ physical interactions to ensure seamless omni-channel banking. Banks can build relationships via merging key technologies such as virtual reality and augmented AI.
Banks can use blockchain to enhance payment processes and lower costs for KYC. Web 3.0 would increase demand for transparency, and banks could follow authentic, transparent data collection practices. This would inform customers of the information shared, and financial institutions could accumulate data to identify opportunities to create solutions for customers’ problems.
Banks could also influence customers by taking a collaborative approach to Web 3.0 compliance. Banking in a secured, fair and equitable way is a key requirement. Thus, banks must find a balance between data usage and AI to support automated lending practices. Inadequate monitoring of tools could be detrimental. By following transformative compliance, banks could differentiate themselves in new markets without facing significant risk.
Banks can influence customers by taking advantage of data mining afforded by Web 3.0, offering a personalised service when they visit the website. Banks can integrate social media into the customer experience so that in real time, they could, for example, send product recommendations based on a customer’s specific need when the customer is checking the website for mortgage information.
Banks can accelerate the loan-providing process through this new technology. Banks traditionally used application forms to collect customer details and evaluate the possibility of providing loans. However, with the help of Web 3.0, lenders will be able to source a vast range of structured data (subject to privacy protection) from multiple sources in real time to unveil interesting insights on borrowers and assess one of the important C’s (character) in analysing creditworthiness.
The biggest threat to Web 3.0 is security; crypto scams and theft result in large losses for financial institutions.
How Acuity Knowledge Partners can help
We use new technology advancements for business upgrades. Our Investment Operations and Risk Services team provides support with data management solutions and supplier and CRM analytics. Our Fund Marketing Support team facilitates digital marketing, providing personalised digital experiences by adopting changes in the marketing environment through Web 3.0. Our Lending Services division helps in lending value-chain processes by using data obtained from data mining. We also provide a number of other solutions and services to clients across the globe.
Sources:
-
https://enlear.academy/web-1-0-vs-web-2-0-vs-web-3-0-e428cfe09dde
-
https://coinmarketcap.com/alexandria/article/what-is-web-3-0
-
https://www.simplilearn.com/tutorials/blockchain-tutorial/what-is-web-3-0
-
https://www.forbes.com/advisor/investing/cryptocurrency/what-is-web-3-0/
-
https://www.intelegain.com/how-will-the-rise-of-web-3-0-benefit-businesses-and-
-
https://www.europeanbusinessreview.com/web-3-0-benefits-for-businesses-the-ultimate-guide/
-
https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2022/07/how-is-web-3-0-shaping-the-future-of-finance
-
https://financialit.net/blog/web-internet-web3/how-web-30-transforming-financial-services-industry
-
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/web-30-impact-banking-biren-parekh?trk=articles_directory
-
https://www.finextra.com/blogposting/7018/web-30-has-enormous-potential-for-banks
-
https://101blockchains.com/web-3-0-blockchain-technology-stack/
-
https://www.emergenresearch.com/industry-report/web-3-market
- https://shardeum.org/blog/what-are-the-features-of-web-3-0/
What's your view?
About the Author
Goshaleea has almost four years working experience in audit, securities market regulation and Lending Servies. Currently she is attached to the Lending Services division at Acuity Knowledge Partners. She is now part of the Acquisition Finance team and responsible for financial analysis of high leveraged borrowers, covenant migration, risk raters, covenant monitoring, credit package creations and other credit workflows for a leading European Bank. Prior to joining Acuity Knowledge Partners, she worked as an Audit Associate in a local audit firm in the audit and assurance and accounting divisions and as an Intern attached to the Supervision division in Securities and Exchange Commission of Sri Lanka. She holds..Show More
Like the way we think?
Next time we post something new, we'll send it to your inbox