Introduction
Introduction
After the global financial crisis in 2008, the roles and responsibilities of central banks have expanded significantly and have become more complex. The banking industry went through a rapid transformation, owing to the emergence of digital technology. Innovation in technologies has enabled banks to offer attractive products and services directly to customers, thus resulting in changes in pricing, transparency, customer convenience and services.
Banks are adjusting their business and day-to-day operational strategies based on customers’ changing behaviors and expectations. This transformation in the financial industry has allowed financial services companies to create new services/ solutions that serve the growing demand of customers.
Neo-banks are offering a new point of view to the banking sector
Neo-banks are digital financial institutions that function without physical branches. In the past, these banks used to collaborate with traditional banks, as they lacked banking licenses. However, regulatory authorities now grant licenses for their banking operations. As they operate digitally, these banks generally have lower operating costs, allowing them to provide advanced services at affordable or low rates.
Various categories of neo-banks cater to the unique needs of each customer in the ever-evolving business landscape
Neo-banks serve various customer segments and offer tailored solutions to meet their specific needs. The following are some common types of neo-banks:
» Front-end neo-banks A front-end neo-bank is a type of bank that does not have a valid banking license to operate on its own. Instead, it partners with a traditional financial institution to provide services to its customers, relying on a financial institution’s support. These neo-banks often rely on the balance sheets of regular banks to carry out their operations.
» Digital banking units Digital banking units are online branches of well-known banks that operate independently. To operate as a stand-alone digital bank, a license for virtual banking is required. Once these banks have enough capital to safeguard the savings of their investors, they can obtain their banking license.
» Full-stack digital banks (licensed) Full-stack digital banks, on the other hand, offer a wide range of services and have the necessary regulatory approvals to operate as banks. They maintain their own separate identities and balance sheets and can provide services such as issuing loans and accepting deposits. Unlike traditional banks, these digital banks are not burdened by expensive physical locations in an increasingly digital world.
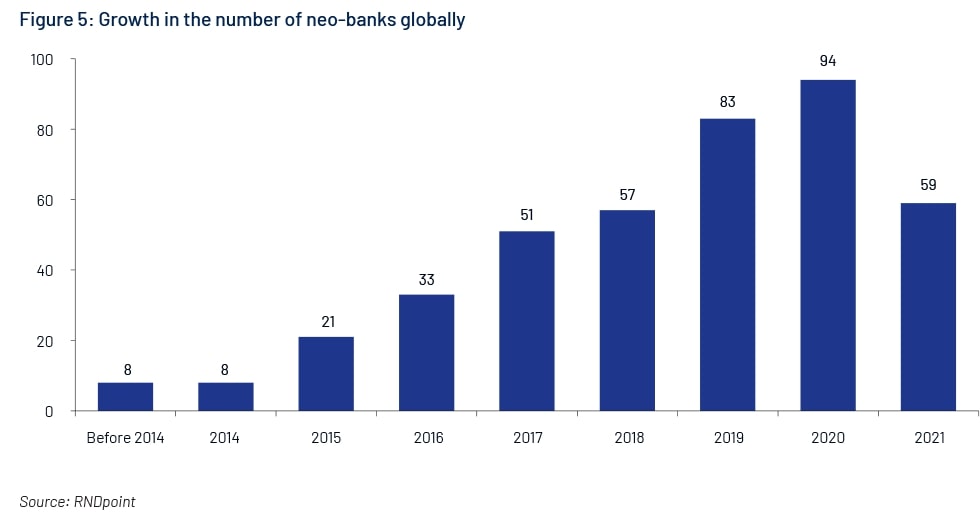
Leading neo-banks globally
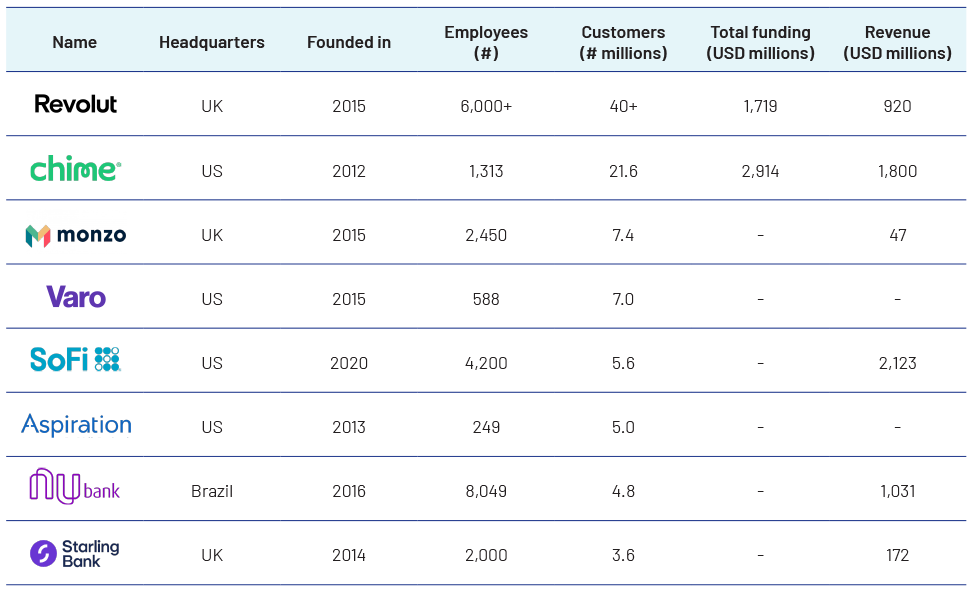
Outlook for neo-banks
The digitization era is most likely here to stay. In a world after the COVID-19 outbreak, traditional banks are expected to increase their investments to enhance technology. Artificial intelligence, internet of things and customer-facing methods (such as CRM software) will likely experience a surge in demand.
Moreover, the financial service sector may likely embrace loan automation, customer support, online account-opening procedures and virtually present call centers through automated or bot chat systems. Neo-banks, leveraging their technological expertise, could serve as a digital interface for core banking solution.
In March 2022, Medici Bank International published “An Analysis of FinTech VC Funding Mega-Rounds in 2021,” stating that neo-banks hold c.12% of total investments. In 29 funding rounds, neo-banks raised USD10bn.
How Acuity Knowledge Partners can add value
Acuity Knowledge Partners has accumulated over two decades of experience and provides services to clients through a vast team of specialists in private markets. Our analysts are well-versed in emerging and established finance areas, assisting clients in the screening, evaluation, and due diligence processes for investments in buyouts, venture capital and private credit. Additionally, we assist in loan origination and related due diligence



